Surgical removal of an intrapulmonary aberrant needle: report of a case
Introduction
Intrapulmonary aberrant needles are relatively rare in clinical practice. An aberrant needle can be transported via the following four routes: transcutaneous, transbronchial, transesophageal, or hematogenous (1,2). Patients with intrapulmonary aberrant needles may have symptoms such as cough, bloody sputum, chest pain, or respiratory distress, but there are also asymptomatic cases that are found accidentally (3). Bronchoscopic removal may be attempted; however, in cases where the needle penetrates into the lungs transbronchially, it may be necessary for patients to undergo surgery (3). We report a case of an intrapulmonary aberrant needle that was removed surgically.
Case presentation
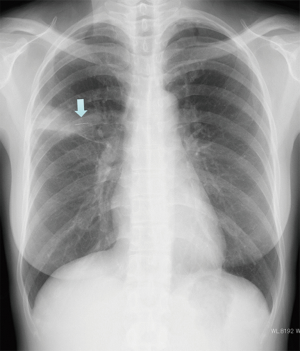
A 44-year-old woman was referred to our hospital with a cough and low-grade fever. A chest X-ray showed a thin, 14-mm-long, metallic-appearing foreign body resembling a sewing needle in the right middle lung field (Figure 1). Chest CT scans showed an abnormal shadow in the bronchial lumen of the right B3a (Figure 2). This shadow had been detected by another hospital 7 years previously, and surgical resection was recommended. However, she had left it without receiving any treatment. She did not have a history of accidental aspiration of the needle or receiving acupuncture.
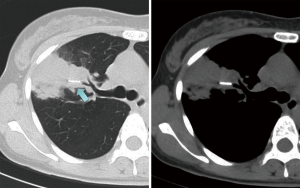
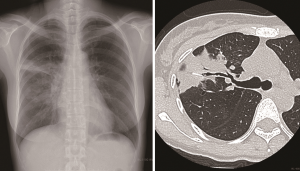
Because bronchoscopic examination revealed that the lumen of the right B3a was occluded by granulation and a whitish structure, we suspected a foreign body. We tried to remove the needle using a forcep under flexible bronchoscopy with rigid bronchoscope. However, because we could not confirm it by bronchoscopic evaluation and bleeding occurred with the forceps maneuver, it was difficult to grasp the needle with a forcep under fluoroscopic guidance. Furthermore, the aberrant needle migrated to the peripheral area of the lung by forceps maneuver (Figure 3). One week later, we performed a video assisted thoracic surgery under fluoroscopic guidance. The aberrant needle was located in the peripheral area of the right S3a, and we confirmed it by fluoroscopy. Because the visceral pleura surrounding the foreign body had granulomatous changes due to inflammation, the needle was not palpable. Therefore, we performed a wedge resection of this area under fluoroscopy. A 14-mm-long, black, rusty needle was observed (Figure 4). The postoperative course was uneventful, and the patient is doing well 12 months after surgery.
Discussion
Intrapulmonary aberrant needles are relatively rare. Miura et al. reviewed 24 surgically resected cases (4). It is considered that intrapulmonary aberrant needles can be transported via the following four routes: transcutaneous, transbronchial, transesophageal, or hematogenous (1,2). In our case, the cause was difficult to determine; however, the route seemed to be transbronchial because the needle was located in the bronchus (B3a). Patients with intrapulmonary aberrant needles may have symptoms such as cough, bloody sputum, chest pain, and respiratory distress, but there are also asymptomatic cases that are found accidentally (3).
An intrapulmonary aberrant needle should be removed as early as possible, even if the patient is asymptomatic (1-6). There have been reported cases in which the intrapulmonary aberrant needle was left for a long period of time, and serious complications such as a lung abscess or empyema developed from inflammatory changes due to foreign body reactions (1,3,7). Most airway foreign bodies were retrieved with bronchoscopy (8,9). On the other hand, because it is difficult to confirm by bronchoscopy, intrapulmonary aberrant needles were removed by surgery in most cases (1-6). If the needle becomes visible, it may be easily removed using a forcep during bronchoscopic examination. However, in our case, it was difficult to grasp the needle by forceps, although we tried to remove it using bronchoscopy. If the needle cannot be directly confirmed, bronchoscopic removal of the foreign body is very difficult, even with fluoroscopic guidance.
When surgically removing the foreign body, the residence period of the aberrant needle in the tissue is important. If the aberrant needle has been present in the body for a long period of time, rust occurs and strongly adheres to the surrounding tissue; additionally, the rusted needle becomes fragile and easy to break at the time of extraction. Therefore, if it is impossible to extract only the needle, partial resection of the lung including the surrounding tissues or segmentectomy may be required (1-4,6). Usami et al. reported the following points as the only conditions under which pulmonary aberrant needles can be excised: (I) the aberrant needle exists near the lung surface; (II) the residence period of the needle in the thoracic cavity is short, and the needle itself has sufficient strength; and (III) the inflammatory adhesion between the lung tissue and needle is mild (6).
In conclusion, we report a case of an intrapulmonary aberrant needle. In such cases, the needle may become rusted and fragile in the lungs. Thus, it is necessary to carefully select the operative procedure when surgically removing an intrapulmonary aberrant needle.
Acknowledgements
Funding: This work was supported in part by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers (C) JP15K10272.
Footnote
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Informed Consent: Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this manuscript and any accompanying images.
References
- Akashi A, Yamamoto G, Ichimiya A, et al. Two resected cases of long-standing intrapulmonary needle over 30 years. Kyobu Gek 1987;40:421-4. [PubMed]
- Motohiro A, Hirota N, Takada S, et al. Surgically removed intrathoracic needle; a report of three cases. J Jpn Assoc Chest Surg 1993;7:685-8. [Crossref]
- Takeshima S, Sensaki K, Marui T, et al. A case of an intrapulmonary needle. J Jpn Assoc Chest Surg 1998;12:539-42. [Crossref]
- Miura H, Taira O, Hiraguri S, et al. Successful surgical removal of an intrapulmonary aberrant needle under fluoroscopic guidance: report of a case. Surg Today 2001;31:55-8. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Ke HY, Tsai CS, Cheng YL, et al. Rare cause of hemoptysis: An intrapulmonary acupuncture needle. J Med Sci 2007;27:237-40.
- Usami N, Mori S, Shigemitsu K, et al. A case of successful removal of an intrapulmonary aberrant needle using video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery. J Jpn Surg Assoc 2004;65:2103-6. [Crossref]
- Jain V, Tiwari S, Misra S, et al. Self-insertion of needles: An unusual cause of empyema thoracis and its thoracoscopic management. J Minim Access Surg 2009;5:108-10. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Blanco Ramos M, Botana-Rial M, García-Fontán E, et al. Update in the extraction of airway foreign bodies in adults. J Thorac Dis 2016;8:3452-6. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Ramos MB, Fernández-Villar A, Rivo JE, et al. Extraction of airway foreign bodies in adults: experience from 1987-2008. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2009;9:402-5. [Crossref] [PubMed]



