Aberrant right subclavian artery in video-assisted thoracoscopic esophagectomy
Introduction
An aberrant right subclavian artery originating from aortic arch was very rare. The reported incidence of such an aberrant varies from less than 1% to 2% (1-3). During normal embryo evolution, the proximal part of right subclavian artery develops from the right fourth primitive aortic arch and the distal from the seventh intersegmental artery (4-6). Formation of abnormal retroesophageal subclavian artery is hypothesized to be the result of the persistence of the intersegmental artery caused by the abnormal involution of the fourth right aortic arch (7,8). When performing video-assisted thoracoscopic esophagectomy, the area at the level above the aortic and in the space between the esophagus and the spine, is usually regarded as a safe area for dissection of upper segment of thoracic esophagus. However, an aberrant right subclavian artery may appear in this area and lead to disastrous complications. We reported a case of aberrant artery encountered during video-assisted thoracoscopic esophagectomy.
Case report
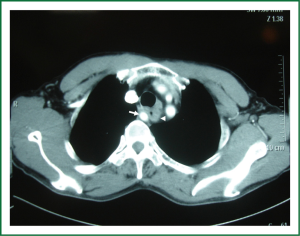
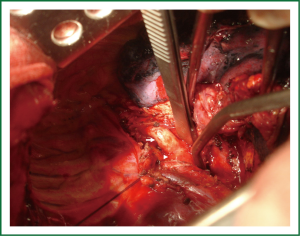
A 57-year-old male was presented to our department with progressive dysphagia for more than 3 months. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy revealed an intraluminal esophageal neoplasm 23 cm distal to his incisor (Figure 1). Biopsy was performed and pathological diagnosis of squamous carcinoma was confirmed. After pre-operative preparation, a video-assisted thoracoscopic esophagectomy was performed through right thoracic approach under double luminal intro-tracheal incubation and general anesthesia. During dissection of upper segment of thoracic esophagus, an aberrant pulsing vessel was encountered the level above aortic arch and in the space between spine and esophagus. In order to investigate this aberrant vessel, the operation was converted to thoracotomy. We identified a retro-esophageal right subclavian artery in a diameter of 1.5 cm (Figure 2), which was thought to be the azygos vein according to a pre-operative enhanced chest CT scan (Figure 1). This artery originates from the aortic arch and parallels to the esophagus. Subsequent operative procedures were then safely performed, and this aberrant artery was kept intact. This patient was discharged on day 8 after operation. At 3 months follow-up, there was no incidence of morbidity.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this the fourth case in published literature describing the aberrant right subclavian artery in patients undergoing esophagectomy (5,8,9). In one case reported by Pantvaidya (8), the aberrant right subclavian artery was transected during video assisted thoracoscopic esophagectomy before being recognized and required an immediate vascular reconstruction via a median sternotomy. Temes (5) and Pramesh (9) reported two cases in whom the aberrant right subclavian artery brings significant difficulty for transhiatal esophagectomy. In the current study, we contributed one more case in the data pool focusing on the significance of aberrant right subclavian artery imposed on esophagectomy. The area in the level above aortic arch and in the space between esophagus and spine is usually believed to be a safe area for dissection of esophagus because there should be no important blood vessels. However, this study and the literature review demonstrated that this ‘safe area’ may have a dangerous vasculature abnormality: the aberrant right subclavian artery. Hence, the presence of this entity has to be kept in mind for every surgeon doing esophagectomy. An intro-operative finding of a large and aberrant pulsing vessel is a warning of encountering such an abnormal artery, and conversion to thoracotomy is necessary when exposure is not satisfying during video assisted thoracoscopic esophagectomy. Prompt reconstruction of a transected aberrant right subclavian artery is also necessary, because 30% to 45% incidence of upper limb ischemia has been documented (10,11).
Pre-operative diagnosis of aberrant right subclavian artery is important but very challenges. This abnormal entity caused no symptoms, although sometimes it may cause dysphagia lusoria and filling defect in barium swallowing when compressing esophagus (3,12,13). However, when associated with esophageal carcinoma, these findings are usually disguised or mixed with those of esophageal tumor, and the aberrant right subclavian artery was confused with azygous vein in preoperative imaging diagnosis (8). After reviewing the chest CT scans of these four patients (5,8,9), we found that the imaging of an enhanced abnormal vascular structure parallel to the esophagus at the level above aortic arch and in the space between esophagus and spine was a common characteristic, which might be used as a valuable diagnostic hint for surgeons having kept this aberrant entity in mind.
Acknowledgements
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Almenar-García V, Terol FF, Correa-Lacarcel J, et al. Retro-esophageal subclavian artery: a case report. Surg Radiol Anat 2002;24:231-4. [PubMed]
- von Segesser L, Faidutti B. Symptomatic aberrant retro-esophageal subclavian artery: considerations about the surgical approach, management and results. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1984;32:307-10. [PubMed]
- Carrozza M, Santoro G, Gaio G, et al. Dysphagia lusoria due to retro-esophageal right subclavian artery in a neonate. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 2007;8:547-8. [PubMed]
- Wind GG, Valentine RJ. eds. Anatomic exposures in vascular surgery. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1991:445-52.
- Temes RT, Tullis MJ, Lee P, et al. Transhiatal esophagectomy in a patient with aberrant right subclavian artery. Ann Thorac Surg 1999;68:2341-2. [PubMed]
- Work WP. Unusual position of the right recurrent laryngeal nerve. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1941;50:769-75.
- Janssen M, Baggen MG, Veen HF, et al. Dysphagia lusoria: clinical aspects, manometric findings, diagnosis, and therapy. Am J Gastroenterol 2000;95:1411-6. [PubMed]
- Pantvaidya GH, Mistry RC, Ghanekar VR, et al. Injury of an aberrant subclavian artery: a rare complication of video assisted thoracoscopic esophagectomy. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2005;11:35-7. [PubMed]
- Pramesh CS, Saklani AP, Parmar V, et al. Aberrant subclavian artery causing difficulty in transhiatal esophageal dissection. Dis Esophagus 2003;16:173-6. [PubMed]
- Lee R, Maughan RE, Svensson LG. Elephant trunk reconstruction for aberrant right subclavian and aortic aneurysm. Ann Thorac Surg 1997;64:547-8. [PubMed]
- Esposito RA, Khalil I, Galloway AC, et al. Surgical treatment for aneurysm of aberrant subclavian artery based on a case report and a review of the literature. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1988;95:888-91. [PubMed]
- Debonnaire G, Verbist J, Peeters P. Dysphagia lusoria. Indications and surgical approaches for non-aneurysmatic aberrant right subclavian artery. Acta Chir Belg 2012;112:237-9. [PubMed]
- Singh S, Grewal PD, Symons J, et al. Adult-onset dysphagia lusoria secondary to a dissecting aberrant right subclavian artery associated with type B acute aortic dissection. Can J Cardiol 2008;24:63-5. [PubMed]


